
The package will now finish adding the repository. After the adding this repository you can update the repository and use the below command to install MySQL. Choose 'debian buster' which has the package 'mysql-server' in it. You'll also be asked to select a repository to add. This is what we want, so use the down arrow to navigate to the Ok menu option and hit ENTER. The defaults will add the repository information for the latest stable version of MySQL and nothing else. The -i flag indicates that we’d like to install from the specified file.ĭuring the installation, you’ll be presented with a configuration screen where you can specify which version of MySQL you’d prefer, along with an option to install repositories for other MySQL-related tools. Note: dpkg is used to install, remove, and inspect.
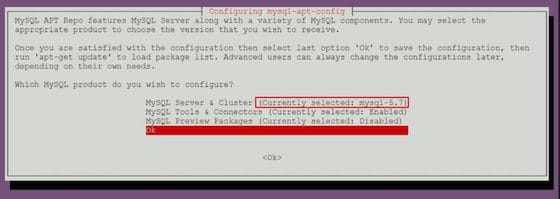
In my case it was: sudo dpkg -i mysql-apt-config_0.8.15-1_all.deb Install the downloaded release package with the following command, replacing version-specific-package-name with the name of the downloaded package (preceded by its path, if you are not running the command inside the folder where the package is): sudo dpkg -i b You can use: sudo wget In my case it was: sudo wget Select and download the release package for your Linux distribution. Go to the download page for the MySQL APT repository at: So to fix this first, add the MySQL server apt repository to your system's software repository list. In Debian 10 for example, MariaDB, a community fork of the MySQL project, is packaged as the default MySQL variant. The issue is caused by the MySQL server apt repository not being included in your system's software repository list. I experienced this issue when trying to install MySQL Server on Debian 10.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
